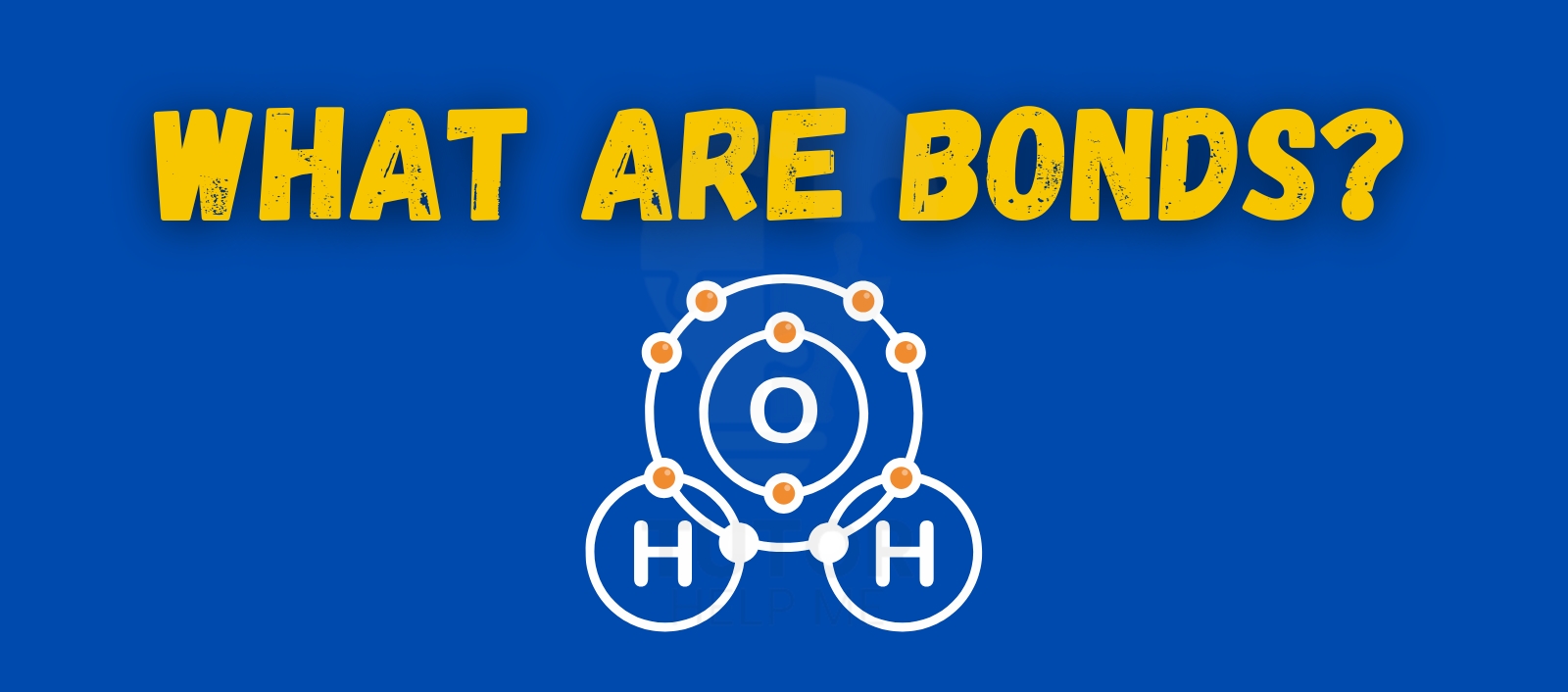
What are bonds? Bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in molecules. They form when atoms share or exchange electrons. Understanding bonds is essential to grasping how substances are built and how they behave.
There are different types of bonds, each with unique properties. These include ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. Each plays a vital role in chemistry and daily life.
In this blog, we will explore the types of bonds and their characteristics. You will discover how these tiny connections impact the world around us. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of bonds together!
what are bonds?
Chemical bonds are connections between atoms that hold molecules together by sharing, transferring, or pooling electrons.
Example,
- Water (H₂O)
Hydrogen and oxygen share electrons. This forms covalent bonds.
Water stays together because of these bonds.
Types of bonds
There are four main types that students must know at GCSE and A-Level:
- Ionic bonds
- Covalent bonds
- Metallic bonds
- Hydrogen bond
Each bond works differently.
Ionic bonds
Ionic bonds form when electrons move from one atom to another.
- One atom loses electrons
- One atom gains electrons
- Opposite charges attract
This usually happens between:
- A metal
- A non-metal
Examples of Ionic Bonds,
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl): Sodium loses one electron to chlorine, forming a positive sodium ion (Na⁺) and a negative chloride ion (Cl⁻). Their attraction creates the ionic bond in table salt.
- Magnesium Oxide (MgO): Magnesium loses two electrons to oxygen, forming a positive magnesium ion (Mg²⁺) and a negative oxide ion (O²⁻). This ionic bond creates a strong crystalline structure.
Learn More about What Is an Ionic Bond? Types, Formation, and Properties
Covalent bonds
Covalent bonds form when atoms share electron pairs to achieve stability.
- Happens between non-metals
- Forms molecules
- Electrons stay shared
Covalent bonds create stable molecules.
Examples of Covalent Bonds,
- Water (H₂O): Each hydrogen atom shares one electron with oxygen, forming two covalent bonds. The shared electrons create a stable molecule essential for life, with oxygen slightly more electronegative.
- Methane (CH₄): Carbon shares one electron with each of four hydrogen atoms, forming four covalent bonds. This sharing creates a stable molecule that serves as a fundamental hydrocarbon in nature.
Learn more about What is covalent bond? Properties and Types Of Covalent Bond
Metallic bonds
Metallic bonds occur when metal atoms share a "sea of electrons" that flow freely around positively charged ions, resulting in strong bonds, high conductivity, and malleability in metals.
- Copper (Cu): Copper atoms share free-moving electrons, creating a metallic bond. This electron flow allows copper to conduct electricity efficiently, making it ideal for wiring and electronic components.
- Iron (Fe): Iron atoms form a metallic bond through a shared electron cloud, giving iron its strength and flexibility. This property makes it essential in construction and manufacturing.
Learn more about What Are Metallic Bonds? Properties and Examples
Hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bonds are weak attractions, not true chemical bonds.
They form when:
- Hydrogen is bonded to oxygen or nitrogen
- Nearby molecules attract each other
- Water (H₂O): Hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen of one water molecule and the oxygen of another. These bonds contribute to water’s unique properties, like high surface tension and boiling point.
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs (adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine) stabilize the double-helix structure, ensuring accurate genetic information transfer during replication and transcription.
Learn more about Hydrogen Bond | Properties and Types of Hydrogen Bonds
How Do Chemical Bonds Affect Physical and Chemical Properties?
Chemical bonds directly influence a substance’s melting and boiling points, electrical conductivity, and solubility.
Key effects:
- Melting point
- Boiling point
- Conductivity
- Solubility
For example:
- Ionic compounds tend to have high melting points and dissolve in water.
- Covalent compounds have lower melting points and may not conduct electricity.
- Metallic bonds provide high conductivity and malleability, making metals useful in electronics and construction.
Common Bond Misconceptions
Many students lose marks here.
- Strong acids ≠ concentrated acids
- Atoms do not disappear in reactions
- Catalysts do not increase yield
- Higher temperature does not always increase yield
- Hydrogen bonds are not ionic or covalent
Fixing misconceptions improves grades fast.
Struggling with bonding concepts is common. Support from a GCSE Chemistry tutor can make these ideas clear and simple.
Exam Tip
Examiners reward:
- Correct keywords
- Short, clear answers
- Accurate definitions
Long answers do not mean more marks.
Choose Tutorhelpme Chemistry Tutors
- Expert Guidance: Highly qualified Chemistry tutors with extensive knowledge of the subject.
- Customized Learning: Tailored lessons to meet individual student needs.
- Flexible Scheduling: Learn at your convenience with adaptable session timings.
- Affordable Rates: Competitive pricing for quality education, starts from £12.
- Interactive Sessions: Engaging and hands-on teaching methods for better understanding.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Assistance with basic to advanced chemistry topics.
- Homework Help: Support for assignments and problem-solving techniques.
- Test Preparation: Guidance for exams like GCSE, A Level, and more.
- One-on-One Tutoring: Personalized attention to address specific challenges.
- Online Accessibility: Learn from the comfort of your home.
- Progress Tracking: Monthly feedback and performance updates.
Learn more about Difference between Ionic Bond and Covalent Bond
FAQ’s
Which bond is strongest?
ionic bonds are strongest among ionic, covalent and hydrogen bonds.
Which bond is unbreakable in chemistry?
Covalent bonds are stable under normal conditions but can break with catalysts or mechanical force.
What are pooling electrons?
Pooling electrons refer to electrons that are shared and move freely between metal atoms.
Can Chemical Bonds Change Over Time?
Yes, bonds can break and reform due to chemical reactions, environmental factors, or external energy influences.
How Are Bonds Affected by Temperature and Pressure?
Temperature and pressure changes can break or strengthen bonds, impacting reactions, phase changes, and material properties.
How Do Bonds Affect a Material’s Properties?
The type of bond determines characteristics such as hardness, melting point, conductivity, and solubility.