Potential energy plays a major role in physics, machines, nature, and everyday life.
This blog will give you a full understanding of what potential energy is, how it works, and why it is important.
You will learn formulas, derivations, types, characteristics, and examples in simple words.
Let’s begin with the basics.
What Is Potential Energy?
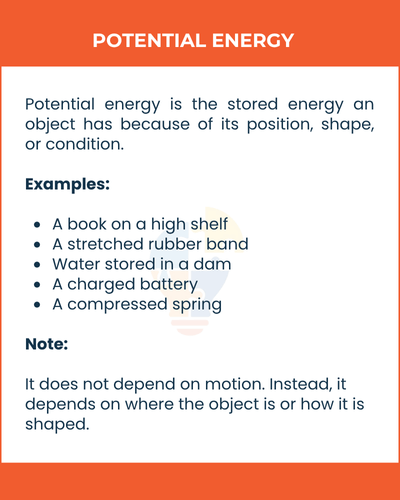
Potential energy is the stored energy an object has because of its position, shape, or condition.
It does not depend on motion. Instead, it depends on where the object is or how it is shaped.
examples
- A book on a high shelf
- A stretched rubber band
- Water stored in a dam
- A charged battery
- A compressed spring
When released, potential energy becomes kinetic energy or other forms.
Potential Energy Formula and Equations
The most common formula for potential energy is gravitational potential energy:
PE = mgh
Where:
- PE = Potential energy (in joules)
- m = mass in kilograms
- g = acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²)
- h = height above ground
Example
A 4 kg box placed 3 m above ground:
PE = 4 × 9.8 × 3 = 117.6J
The box has 117.6 joules of potential energy.
Deriving the Potential Energy Formula
Potential energy is linked to the work done against gravity.
Step 1: Work formula
Work = Force × Distance
Step 2: Force against gravity
F = mg
Step 3: Multiply by height
Work = mg × h
This work becomes stored energy:
PE = mgh
Thus, potential energy represents the energy stored due to position.

Types of Potential Energy
Potential energy appears in different forms depending on the situation. Here are the main types explained in simple terms.
Gravitational Potential Energy
This energy is stored when an object is lifted to a height.
Key idea
Higher position = more gravitational potential energy.
Formula
PE = mgh
Examples
- A rock on a hill
- A child on a slide platform
- Water ready to fall in waterfalls
- Airplane at a high altitude
- A fruit on a tree branch

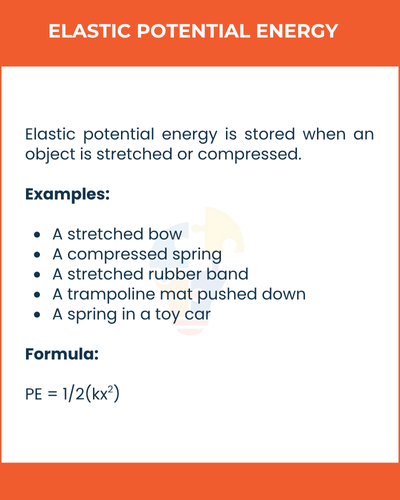
Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy is stored when an object is stretched or compressed.
Examples
- A stretched bow
- A compressed spring
- A stretched rubber band
- A trampoline mat pushed down
- A spring in a toy car
Formula
PE = 1/2(kx2)
Where:
- k = spring constant
- x = extension or compression
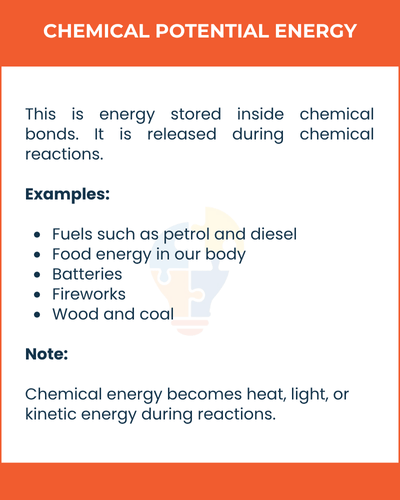
Chemical Potential Energy
This is energy stored inside chemical bonds. It is released during chemical reactions.
Examples
- Fuels such as petrol and diesel
- Food energy in our body
- Batteries
- Fireworks
- Wood and coal
Chemical energy becomes heat, light, or kinetic energy during reactions.
Electrical Potential Energy
Electrical potential energy is stored when electric charges are separated.
Examples
- A charged capacitor
- Lightning clouds
- Electric fields around charges
- Energy stored in batteries
- Static electricity shocks
Formula
PE = qV
Where:
- q = charge
- V = electric potential

Characteristics of Potential Energy
Potential energy has important characteristics that make it useful in physics.
Stored Energy
Potential energy stays stored until released.
Example
A book placed on a shelf stores energy until it falls.
Depends on Position or Shape
Different heights or shapes store different amounts of potential energy.
Example
A stretched bow stores more energy than a slightly stretched one.
Converts Into Other Energies
Potential energy easily converts to kinetic, heat, sound, or electrical energy.
Examples
- Waterfall: potential → kinetic → electrical
- Pendulum: potential ↔ kinetic
- Battery: chemical → electrical
Increases With Height
More height means more gravitational potential energy.
Example
A rock at 10 m has more potential energy than the same rock at 2 m.
Can Be Zero
An object at ground level can have zero potential energy depending on reference level.
Can Exist Without Motion
This is what makes potential energy different from kinetic energy.
Depends on Mass
Heavier objects have more potential energy at the same height.
Real-Life Uses of Potential Energy
Potential energy plays a role in many useful processes:
Daily life
- Lifting objects
- Clocks using springs
- Archery
- Roller coasters
Nature
- Water cycle
- Fruit falling
- Snow avalanches
Engineering
- Dams generating electricity
- Springs in machines
- Batteries in devices
Biology
- Food energy used by the body
Potential energy is everywhere around us.
Potential Energy vs Kinetic Energy
| Potential Energy | Kinetic Energy |
|---|---|
| Stored energy | Energy of motion |
| Depends on position or shape | Depends on mass and speed |
| No movement required | Requires movement |
| Example: stretched spring | Example: moving car |
Understanding both helps explain how energy moves and changes.
Conclusion
Potential energy is one of the most important ideas in physics. It explains how energy can be stored and later released to produce motion, heat, electricity, and many other forms of energy.
From the height of a rock to the stretch of a bow, to the charge in a battery, potential energy helps us understand how nature and machines work.
Knowing what potential energy is, how to calculate it, and how it changes makes learning physics easier and more useful in daily life.
Read More What Is Kinetic Energy? Formula & Derivation
FAQs
What is potential energy?
It is stored energy based on position, height, shape, or condition.
What unit is used?
Joules (J).
What two factors affect gravitational potential energy?
Mass and height.
What is the formula for potential energy?
PE = mgh.
Do all objects have potential energy?
Yes, if they have position, shape, or chemical structure.
Is chemical energy potential energy?
Yes. It is stored in chemical bonds.
What energy does a stretched rubber band store?
Elastic potential energy.
What happens when potential energy is released?
It converts into kinetic or other energy.
Does gravity affect potential energy?
Yes. More gravity means more potential energy.
Is potential energy always positive?
It depends on the reference point, but usually yes.
What is the difference between elastic and gravitational potential energy?
Elastic depends on shape; gravitational depends on height.
What is the potential energy of an object at ground level?
It can be zero if the ground level is reference point.
Is battery energy potential energy?
Yes, electrical potential energy.
Does stretching increase potential energy?
Yes. More stretch = more stored energy.
Can potential energy turn into heat?
Yes, during friction.
Does a book on a shelf have energy?
Yes, gravitational potential energy.
Why does a higher object have more potential energy?
It has more ability to do work when falling.
Can potential energy exist at rest?
Yes. No motion is required.
What is the potential energy of flowing water?
Before flowing, water in a dam stores potential energy.
Do springs store potential energy?
Yes, elastic potential energy.

