Knowing the difference between a mole and a molecule is easier than it seems. A mole counts tiny particles like atoms. A molecule is a group of connected atoms.
Moles help us count things we can’t see. Molecules make up everything around us. Both are important in understanding science.
In this guide i will explain What is mole and molecule? simply. Let’s learn about them step by step!
What is Mole?
A mole is a standard unit in chemistry used to measure the amount of a substance. It represents 6.022 × 1023 particles (atoms, molecules, or ions).
Unit of Mole
The SI unit of a mole is mol.
Formula for Mole
Mole = Mass of Substance (g) ÷ Molar Mass (g/mol)
Example of Mole
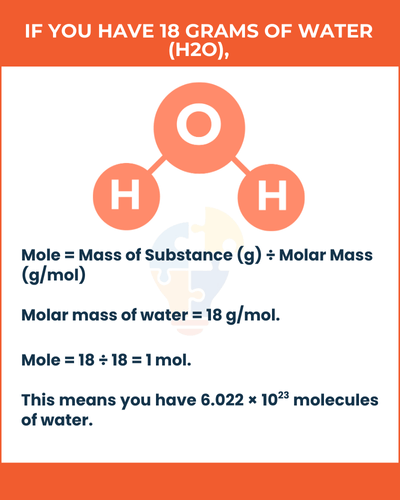
If you have 18 grams of water (H2O), calculate the number of moles:
- Molar mass of water = 18 g/mol.
- Mole = 18 ÷ 18 = 1 mol.
This means you have 6.022 × 1023 molecules of water.
What is Molecule?
A molecule is the smallest unit of a chemical compound that retains its chemical properties. It consists of one or more atoms bonded together.
Types of Molecules
- Monoatomic Molecules: Single atoms acting as molecules (e.g., noble gases like He, Ne).
- Diatomic Molecules: Contain two atoms (e.g., O2, H2).
- Polyatomic Molecules: Contain more than two atoms (e.g., CO2, H2O).
- Complex Molecules: Large structures like proteins or DNA.
Unit of Molecule
Molecules are counted in moles, using 6.022 × 1023 particles as a reference.
Formula for Molecule Counting
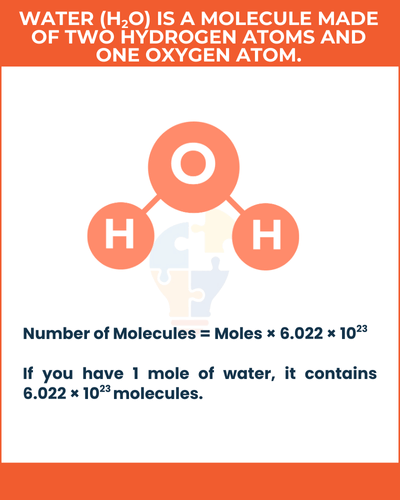
Number of Molecules = Moles × 6.022 × 1023
Example of a Molecule
Water (H2O) is a molecule made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. If you have 1 mole of water, it contains 6.022 × 1023 molecules.
Mole vs Molecule
| Aspect | Mole | Molecule |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A unit used to measure the quantity of a substance, defined as 6.022×1023. | The smallest unit of a compound, consisting of two or more bonded atoms. |
| Purpose | Measures the amount of particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) in a substance. | Represents the actual physical structure of bonded atoms in a substance. |
| Composition | A mole does not describe specific structures; it is purely a counting unit. | Describes the arrangement and bonding of atoms (e.g., O2, H2O). |
| SI Unit | SI Unit is mol. | Molecules don’t have an SI unit but are counted using moles. |
| Formula | Number of Particles = Moles × 6.022 × 1023 | No specific formula for a molecule; instead, chemical formulas represent molecules (e.g., CO2). |
| Example | 1 mole of water contains 6.022 × 1023 water molecules. | A water molecule (H2O) is made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. |
| Types | Mole applies universally to atoms, ions, or molecules as a counting unit. | Types of molecules include monoatomic, diatomic, polyatomic, and complex molecules. |
| Use in Chemistry | Helps in stoichiometric calculations, defining molar mass, and understanding reactions. | Describes how atoms combine to form chemical substances, essential in understanding properties. |
Why Choose Tutorhelpme Chemistry Tutors?
- Experienced Tutors: Learn from experts Chemistry tutors with deep subject knowledge and teaching experience.
- Personalised Support: Tailored lessons to meet your unique learning needs and goals.
- Exam Preparation: Effective strategies and resources to help you excel in exams.
- Interactive Sessions: Engage in dynamic, one-on-one online lessons for better understanding.
- Affordable Rates: Get quality tutoring without straining your budget.
- Wide Coverage: Assistance with basic concepts to advanced Chemistry topics.
- Convenient Learning: Study from the comfort of your home at flexible times.
- Proven Results: Many students have improved their grades with our support.
Read More What is Density? (Unit, Formula, Types)
FAQs
How many atoms is 1 mole?
One mole contains 6.022×1023 atoms, known as Avogadro’s number, representing the amount of particles in one mole.
How to convert molecules to moles?
To convert molecules to moles, divide the given number of molecules by Avogadro’s number 6.022×1023.
How many moles are in 25g of NaCl?
Moles = Mass ÷ Molar Mass. For NaCl: 25 ÷ 58.44 = about 0.43 moles, using molar mass calculation.
Are moles bigger than molecules?
Yes, a mole is a unit measuring quantity, while a molecule is a single particle. Mole represents many molecules.

