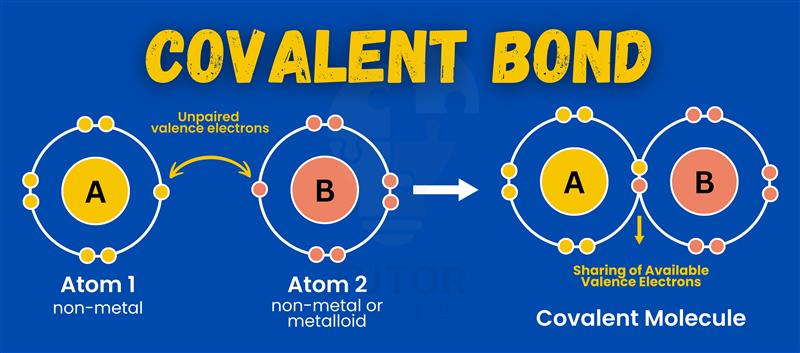
A covalent bond forms when atoms share electrons to become stable. It is common in non-metal compounds like water. Covalent bonds differ in strength and properties based on electron sharing.
There are different types, each with unique characteristics that impact a substance’s behaviour. Knowing these helps in understanding chemical reactions and bonding patterns.
Let’s explore What is covalent bond, its properties, and types of covalent bond to make complex ideas easy and clear.
What is Covalent Bond?
A covalent bond forms when two atoms share electrons to achieve stability.
Example,
In a water molecule (H₂O), oxygen shares electrons with two hydrogen atoms.
Properties of Covalent Bond
- Formation: Covalent bonds form when atoms share electron pairs to achieve stability.
- Bond Strength: These bonds are strong but generally weaker than ionic bonds.
- Directionality: Covalent bonds are directional, occurring specifically between the atoms involved.
- Molecular Nature: Compounds formed are typically molecular rather than lattice-like.
- Melting and Boiling Points: Usually low due to weaker intermolecular forces.
- Electrical Conductivity: Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity, as they lack free ions or electrons.
- States of Matter: Found in solids, liquids, and gases at room temperature.
- Solubility: Often soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water.
- Bond Length: The distance between bonded atoms is precise and contributes to molecular stability.
- Bond Polarity: Can be polar or non-polar, depending on the electronegativity difference between atoms.
- Reactivity: Reactivity varies based on bond strength and molecule type.
- Flexibility: Covalent bonds allow the formation of flexible, stable molecular structures.
- Examples: Found in essential molecules like water (H₂O), oxygen (O₂), and methane (CH₄).
Covalent bonds are fundamental in creating organic compounds and supporting life processes, ensuring molecular diversity and stability.
Read more about what are bonds? types of bonds
Types of Covalent Bond
These are the types of covalent bonds:
- Single covalent bond
- Double covalent bond
- Triple covalent bond
- Nonpolar covalent bond
- Polar covalent bond
Single covalent bond
A single covalent bond forms when two atoms share one pair of electrons.
Example,
In a hydrogen molecule (H₂), each hydrogen atom shares one electron.
Properties of Single Covalent Bond
- Forms when two atoms share one electron pair.
- Typically found in nonmetals like H₂, Cl₂, and CH₄.
- Weakest strength compared to double and triple bonds.
- Has longer bond length than double or triple bonds.
- Found in molecules with stable electronic configurations.
- Allows free rotation around the bond axis.
- Common in organic compounds.
- Contributes to molecular flexibility.
- Usually nonpolar unless formed between different elements.
- Easy to break during chemical reactions.
“Our 1-on-1 Chemistry Tutors can help you stay on track and build confidence.”
Double covalent bond
A double covalent bond forms when two atoms share two pairs of electrons.
Example,
In an oxygen molecule (O₂), two oxygen atoms share two electron pairs.
Properties of Double Covalent Bond
- Involves sharing of two electron pairs between atoms.
- Found in molecules like O₂ and CO₂.
- Stronger than single bonds but weaker than triple bonds.
- Has intermediate bond length.
- Prevents rotation, leading to rigidity in molecules.
- Commonly observed in carbon-based compounds.
- Increases molecular stability compared to single bonds.
- Often polar when between different atoms.
- Requires more energy to break than single bonds.
- Affects molecular shape and reactivity.
Triple Covalent Bond
A triple covalent bond forms when two atoms share three pairs of electrons.
Example,
In a nitrogen molecule (N₂), two nitrogen atoms share three electron pairs.
Properties of Triple Covalent Bond
- Forms when atoms share three electron pairs.
- Found in molecules like N₂ and C₂H₂.
- Strongest and shortest bond type among covalent bonds.
- Highly rigid with no rotation around the bond.
- Commonly found in unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- Adds high stability to molecules.Often polar in compounds like HCN.
- Requires significant energy to break.
- Influences molecular geometry significantly.
- Leads to high electron density between bonded atoms.
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
A nonpolar covalent bond occurs when electrons are shared equally between two atoms.
Example,
In a chlorine molecule (Cl₂), electrons are evenly shared.
Properties of Nonpolar Covalent Bond
- Forms when atoms share electrons equally.
- Found in molecules like O₂, H₂, and CH₄.
- Exhibits no dipole moment as electron distribution is uniform.
- Occurs between identical or similar atoms.
- Weak intermolecular forces like London dispersion forces.
- Results in low boiling and melting points.
- Insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents.
- Generally nonreactive under normal conditions.
- Essential for forming stable molecular structures.
- Allows free movement of atoms within the molecule.
Polar Covalent Bond
A polar covalent bond occurs when electrons are shared unequally between two atoms.
Example,
In water (H₂O), oxygen pulls electrons closer than hydrogen.
Properties of Polar Covalent Bond
- Occurs when electrons are shared unequally.
- Found in molecules like H₂O and HCl.
- Creates partial positive and negative charges on atoms.
- Exhibits a dipole moment due to electron density shift.
- Stronger than nonpolar covalent bonds.
- Soluble in polar solvents like water.
- Affects molecular polarity and reactivity.
- Leads to hydrogen bonding in certain compounds.
- Influences boiling and melting points significantly.
- Plays a vital role in biochemical interactions.
Why Choose Tutorhelpme Chemistry Tutors
- Expert Guidance: Chemistry tutors with deep knowledge of chemistry concepts and applications.
- Simplified Explanations: Learn difficult topics in an easy-to-understand way.
- Personalised Support: Tailored lessons to match your learning pace and goals.
- Proven Results: Boost grades and understanding with effective teaching strategies.
- Affordable Rates: Quality tutoring at competitive prices, starts from £15.
- Exam Preparation: Comprehensive support for GCSE, A-Level, and university exams.
- Flexible Learning Options: Online sessions for convenience and accessibility.
- Interactive Approach: Engaging lessons with practical examples and problem-solving.
- Trusted Service: Positive reviews from satisfied students and parents.
Read More Difference between Ionic Bond and Covalent Bond
FAQs
What is covalent bonding?
It is when atoms share electrons to become stable.
Which elements form covalent bonds?
Non-metals form covalent bonds with each other.
Do covalent compounds conduct electricity?
No, because they have no free ions or electrons.
Why do covalent compounds have low melting points?
Because weak forces act between molecules.
How many electrons are shared in a double bond?
Two pairs (four electrons) are shared.