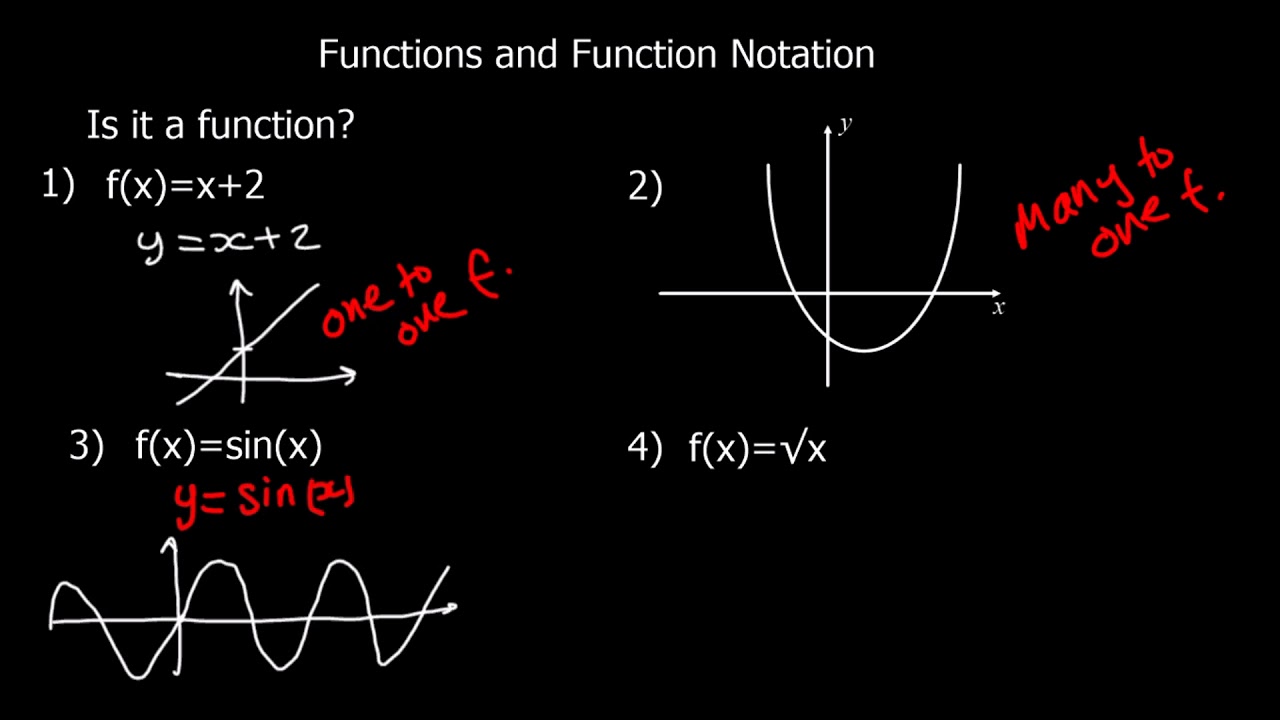
A function in maths is a rule that gives exactly one output for each input.
To put it simply, a function is a relationship in which each input has a specific relationship to one output. Each function has a domain, codomain, and range.
The general notation for a function is f(x), where x represents the input. A function is generally represented as y = f(x).
What is a Function in Maths?
A Function in Maths is a unique relationship between inputs (also referred to as the domain) and their outputs (also referred to as the codomain) in which each input has one output that can be linked back to its input.
“Book a free Assessment for Maths Tutor“
What is a Function in Algebra?
A function in algebra assigns each input a unique output. It’s a relationship where one variable depends on another.
Example:
The equation f(x)=2x+3 represents a function. For any x, it provides a single, specific f(x).
What is an Inverse Function?
An inverse function reverses the original function's operation, mapping outputs back to inputs while maintaining a one-to-one correspondence.
Example:
For f(x) = 2x+3,
The inverse is f−1(x) = x−3 ÷ 2
If f(4) = 11,
Then f−1(11) = 4
Domain and Range in Functions
These are key GCSE and A Level concepts.
Domain in functions
The domain is all possible input values.
Example:
f(x) = 2x + 1
Domain = all real numbers
Range in functions
The range is all possible output values.
Example:
If x = 1, 2, 3
Range = 3, 5, 7
Understanding domain and range helps students interpret functions correctly.
Types of Functions in Maths
The following are the types of Function in Maths :
- 1. One-to-One Function
- 2. Many-to-One Function
- 3. Onto Function
- 4. One – One and Onto Function
One-to-One Function
A one to one function is a unique function in which each element of the range is mapped to exactly one element of its domain i.e, the outputs are never repeated.
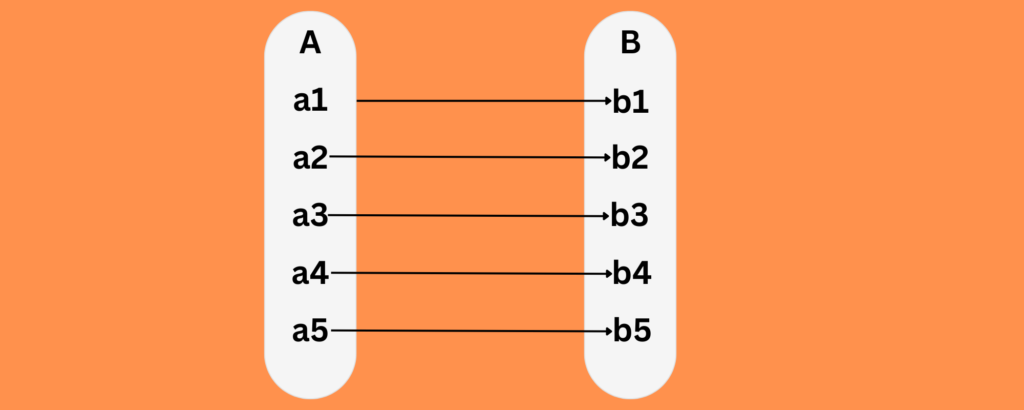
Example
Let’s use the function f(x)=3x−2
Assume f(a1)=f(a2)
So, 3a1−2 = 3a2−2
Simplify: 3a1−2=3a2−2 which implies 3a1=3a2
Further simplify: a1=a2
Since a1 must equal a2 when f(a1)=f(a2), this function is indeed one-to-one.
- For x=1 : f(1)=3(1)−2=1
- For x=2 : f(2)=3(2)−2=4
- For x=3 : f(3)=3(3)−2=7
X-axis: Represents input values
Y-axis: Represents output values f(x).
Many-to-One Function
This function transfers one or more elements from set A to an same element in set B. The same image appears in B for two or more of A's elements.
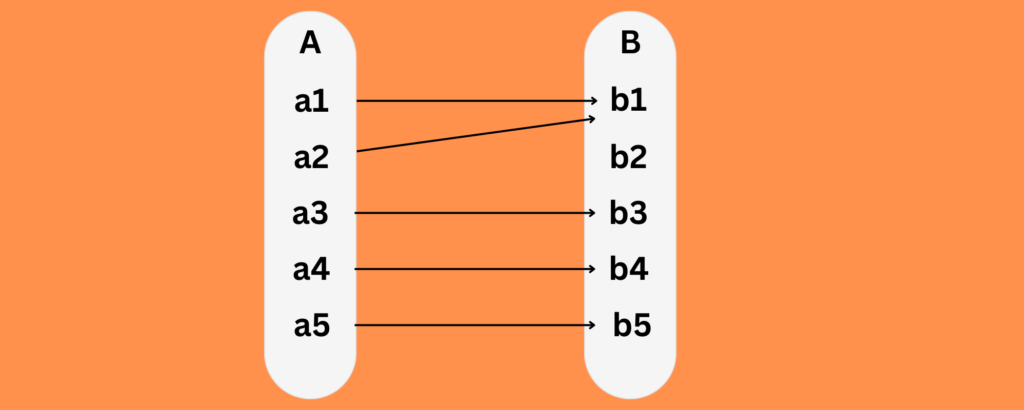
Example
f(x)=x2
x=2 and x=-2
For x=2 ,
f(2)=22=4
For x=−2
f(−2)=(−2)2=4
Onto Function
Onto function could be explained by considering two sets, Set A and Set B, which consist of elements. If for every element of B, there is at least one or more than one element matching with A, then the function is said to be onto function
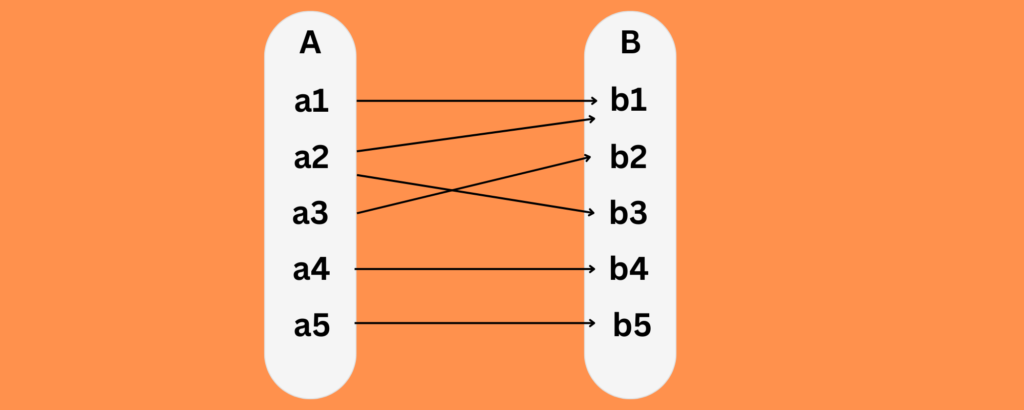
Example
f: R→R
Domain: R (all real numbers)
Codomain: R (all real numbers)
To show that this function is onto, we need to demonstrate that for every y∈Ry \in \mathbb{R}y∈R, there exists an
x∈R such that f(x)=yf(x) = yf(x)=y
Start with f(x)=y
Substitute f(x)with 2x+1
2x+1=y
Solve for x:
2x=y−1
x= y−1 / 2
Since for every y there exists an x (specifically x=y−1 / 2), f(x)=2x+1 is an onto function.
One – One and Onto Function
Function, f is One – One and Onto or Bijective if the function f is both One to One and Onto function. In other words, the function f associates each element of A with a distinct element of B and every element of B has a pre-image in A.
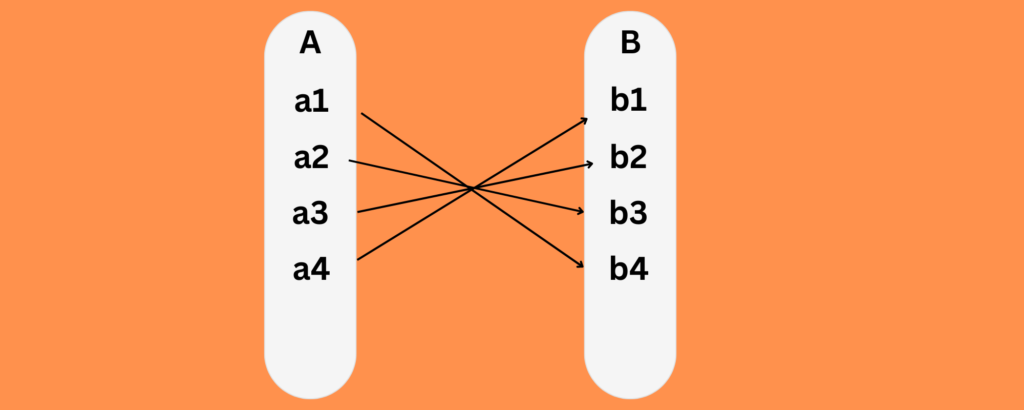
Function: f:{1,2,3}→{a,b,c} defined by:
f(1)=a
f(2)=b
f(3)=c
- Each element of the domain maps to a unique element in the codomain.
- No two domain elements map to the same codomain element.
Conclusion: f is one-to-one.
- Every element in the codomain {a,b,c} is covered.
- a, b, and c are all mapped by 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
Conclusion: f is onto.
Overall: The function f is both one-to-one and onto.
How to Find the Minimum or Maximum Value of a Function
How To Find the Minimum Value of a Function
Given the Function : f(x)=x2−4x+3
- Find the derivative:
f′(x)=2x−4 - Set the derivative equal to zero:
2x−4=0
x=2x - Check the second derivative:
f′′(x)=2
Since the second derivative is positive, the function has a minimum at x=2. - Find the minimum value:
Substitute x=2 back into the original function:
f(2)=(2)2−4(2)+3=1
Thus, the minimum value of the function is 1 at x=2.
How To Find the Maximum Value of a Function
Given the Function : f(x)=−x2+4x+1
- Find the derivative:
f′(x)=−2x+4 - Set the derivative equal to zero:
−2x+4=0
x=2 - Check the second derivative:
f′′(x)=−2
Since the second derivative is negative, the function has a maximum at x=2 - Find the maximum value:
Substitute x=2 back into the original function:
f(2)=−(2)2+4(2)+1=5
Thus, the maximum value of the function is 5 at x=2.
Why Functions Are Important in Maths
Functions are used in many GCSE and A Level topics:
- Algebra
- Graphs
- Calculus
- Trigonometry
- Physics and science
They help model real-world relationships.
Functions form the foundation of advanced maths.
Many students struggle with functions due to weak algebra skills. Our GCSE Maths tutors help students master functions step-by-step using exam-focused methods.
Common GCSE Function Questions
Students are often asked to:
- Find f(x) for a given value
- Solve equations using functions
- Interpret function graphs
- Find inverse functions
- Identify the domain and range
These skills are essential for exams.
Common Mistakes Students Make
Students often:
- Forget to apply the full rule
- Misunderstand function notation
- Confuse functions with equations
- Make algebra errors
- Struggle with inverse functions
These mistakes reduce exam marks.
Structured practice helps avoid these errors.
How TutorHelpMe Helps Students Master Functions
TutorHelpMe GCSE and A Level maths tutors teach functions step-by-step.
Students learn:
- Function notation clearly
- How to evaluate functions
- Graph interpretation
- Exam question techniques
- Inverse functions and composite functions
Lessons focus on building strong understanding and exam confidence.
Many students improve grades significantly after mastering functions.
Read More What Is A Range In Math?
FAQs
What is function notation?
Function notation is written as f(x). It shows the output of a function for input x.
Example:
f(x) = x²
How do you solve functions?
Substitute the input value into the function and simplify.
Example:
f(x) = 3x
f(5) = 15