Want to understand how things move and why they stop? Learning about forces makes it simple.
We use and feel different types of forces every day when we open a door, lift a bag, or ride a bike.
This guide will walk you through the most common types of forces like gravity, friction, and tension, using real-life examples that are easy to follow.
Sit back, have a cup of tea, Let’s explore the basic types of forces that make things around us work.
What Are the Two Main Categories of Forces?
Forces are classified into two categories:
Contact Forces – These require physical contact between objects.
Examples, include friction, tension, and applied force.
Non-Contact Forces – These act at a distance without direct contact.
Examples, include gravity and electromagnetic force.
Both types of forces play a crucial role in motion and stability.
Types of Forces
Forces are a part of everything we do. They influence how things move, stop, or stay in place. In simple terms, a force is a push or pull that acts on an object. Let’s explore the different types of forces and see how they work in our daily lives.
Gravitational Force
Why does gravity exist? Gravitational force pulls things toward Earth. It gives objects weight and keeps them from floating away.
Example,
You see gravity in action when a ball falls to the ground. Without it, the ball would stay in the air. Gravity also keeps your feet on the ground when you walk.
Another Real-Life Scenario,
Think about riding a roller coaster. As it goes up, you feel light. As it drops, gravity pulls you down fast. That’s what makes the ride exciting.

Now that you know how gravity works, let’s look at another everyday force, friction.
Frictional Force
How does friction affect motion? Frictional force happens when two surfaces touch. It pushes against movement and helps slow things down.
Example,
You can feel friction when you rub your hands together. They get warm because friction makes heat. This shows how strong and useful friction is in daily life.
Another Real-Life Scenario,
Think about driving a car. Tyres grip the road with the help of friction. It lets you stop, turn, and stay safe. Without it, the car would slide.

Now that you know how friction helps control motion, let’s see how tension force works to pull and hold things in place.
Tension Force
Tension is a force that moves through a rope, string, or cable when you pull it tight. It helps hold things up or keep them together.
Example:
You see tension when you hang a picture frame with a rope. The rope pulls upward, keeping the frame steady and in place. This shows how tension holds weight.
Another Real-Life Scenario,
Flying a kite also shows tension. As you pull the string, it becomes tight. That tension keeps the kite steady, even when the wind blows hard.

Now that you’ve seen how tension keeps things connected, let’s look at normal force, the force that pushes up when objects rest on a surface.
Normal Force
How does normal force work? It is the support force given by a surface. It pushes straight up on the object resting on it.
Example:
You feel normal force when you sit on a chair. The chair pushes up to balance your weight. This shows how normal force works against gravity to hold you up.
Another Real-Life Scenario,
Place a cup on a table. The table pushes up with normal force to support the cup. Without it, the cup would fall.

Now that you understand how surfaces support objects, let’s learn about applied force, the force you use to move things around.
Applied Force
Applied force is the push or pull you use to move something. It comes from a person or an object in action.
Example:
You use applied force when you open a door. The more force you use, the quicker it opens. This shows how applied force controls movement.
Another Real-Life Scenario,
Think about pushing a shopping trolley. You control its speed by changing how much force you apply. It’s a clear example of how force works in daily life.
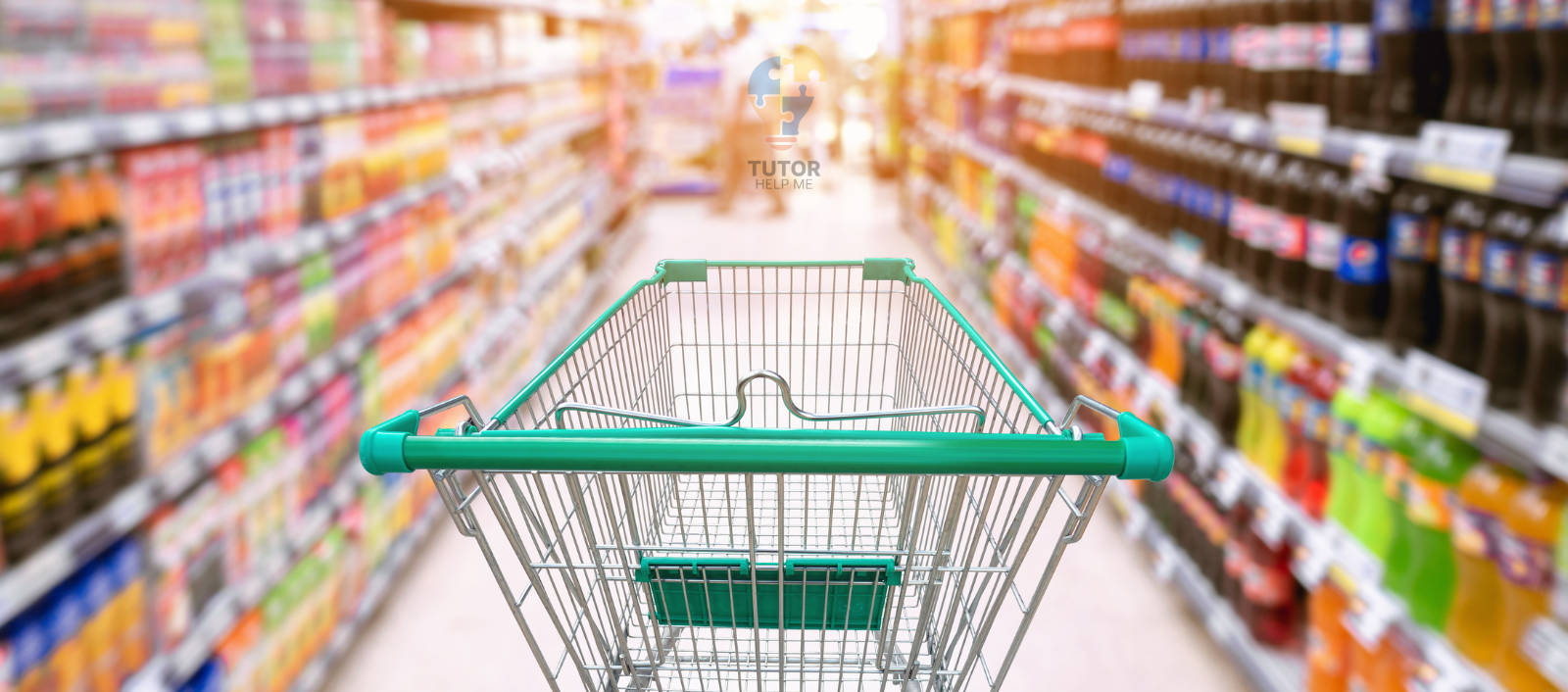

Now that you know how we use force to move things, let’s learn about electromagnetic force, a powerful force behind magnets and electricity.
Electromagnetic Force
Why are electromagnetic forces important? They act between charged particles and control how electricity and magnetism work.
Example:
You see this force when you turn on a light. The electricity flows through wires because of electromagnetic force, making the bulb glow.
Another Real-Life Scenario,
A fridge magnet also shows this force. The magnet sticks firmly because the electromagnetic force pulls it to the metal surface.
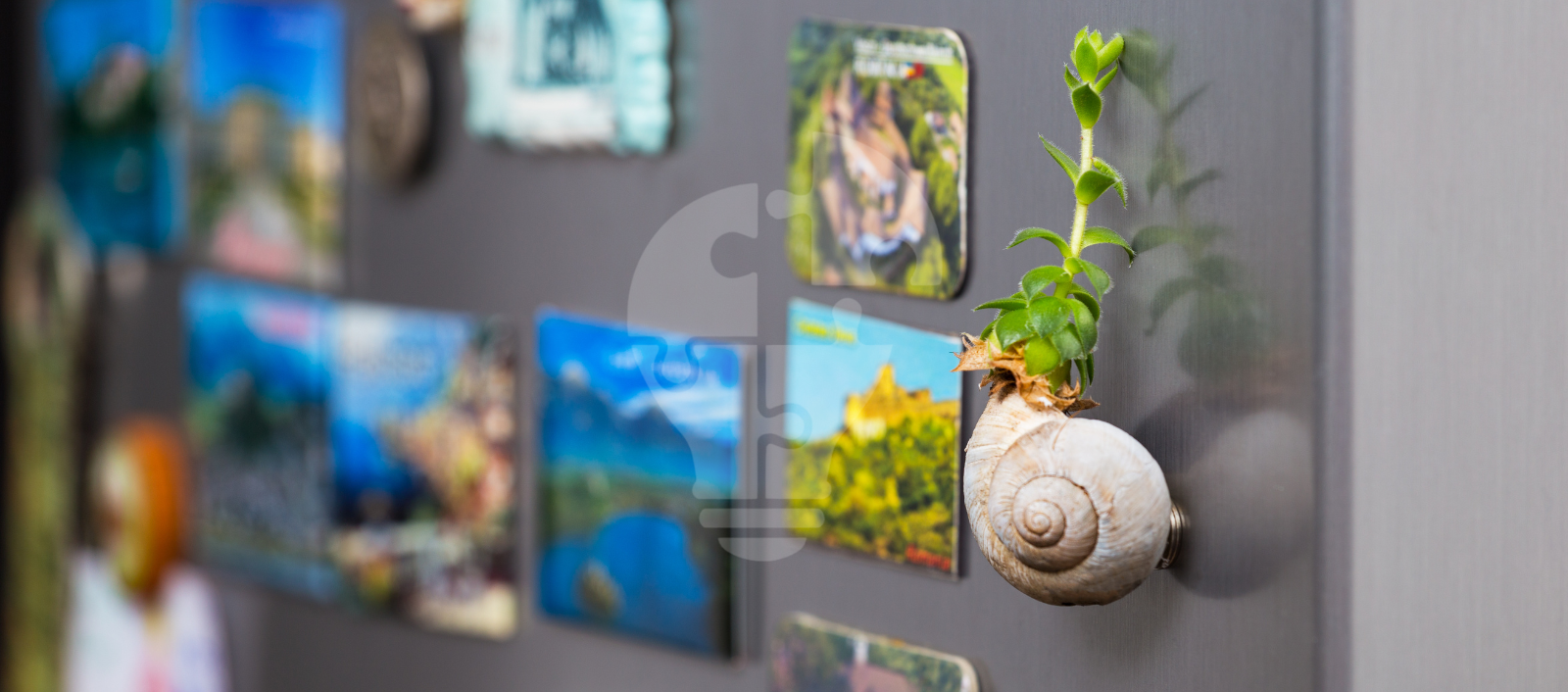

Now that you’ve seen how this invisible force powers devices and holds magnets, let’s look at spring force—the force that makes things stretch and bounce back.
Spring Force
How does a spring store energy? Spring force appears when you stretch or press a spring. It works to return the spring to its normal shape.
Example:
You feel this force when you bounce on a trampoline. The springs stretch and then snap back, pushing you into the air.
Another Real-Life Scenario,
Clicking a pen shows the same force. You press the button and a spring inside gets squeezed. When you let go, spring force pops the button back up.
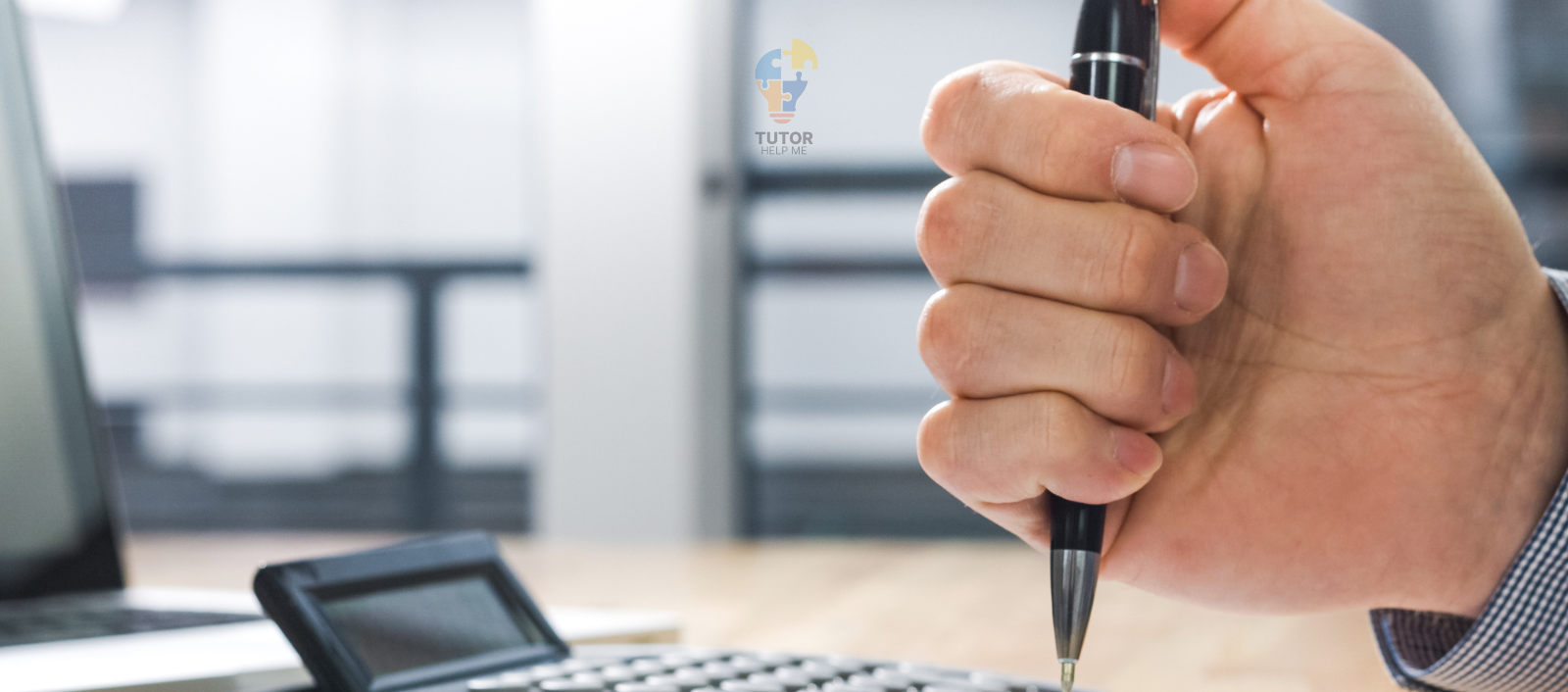

Now that you know how springs store and release energy, let’s explore air resistance—a force that pushes against things moving through air.
Air Resistance
What is the role of air resistance in motion? It is a frictional force that pushes against objects moving through the air.
Example:
You feel this when cycling fast on a windy day. The air pushes back and makes it harder to move. That’s air resistance slowing you down.
Another Real-Life Scenario,
Parachutes use this force to work. As a person falls, the parachute opens and creates drag. This slows the fall and helps them land safely.
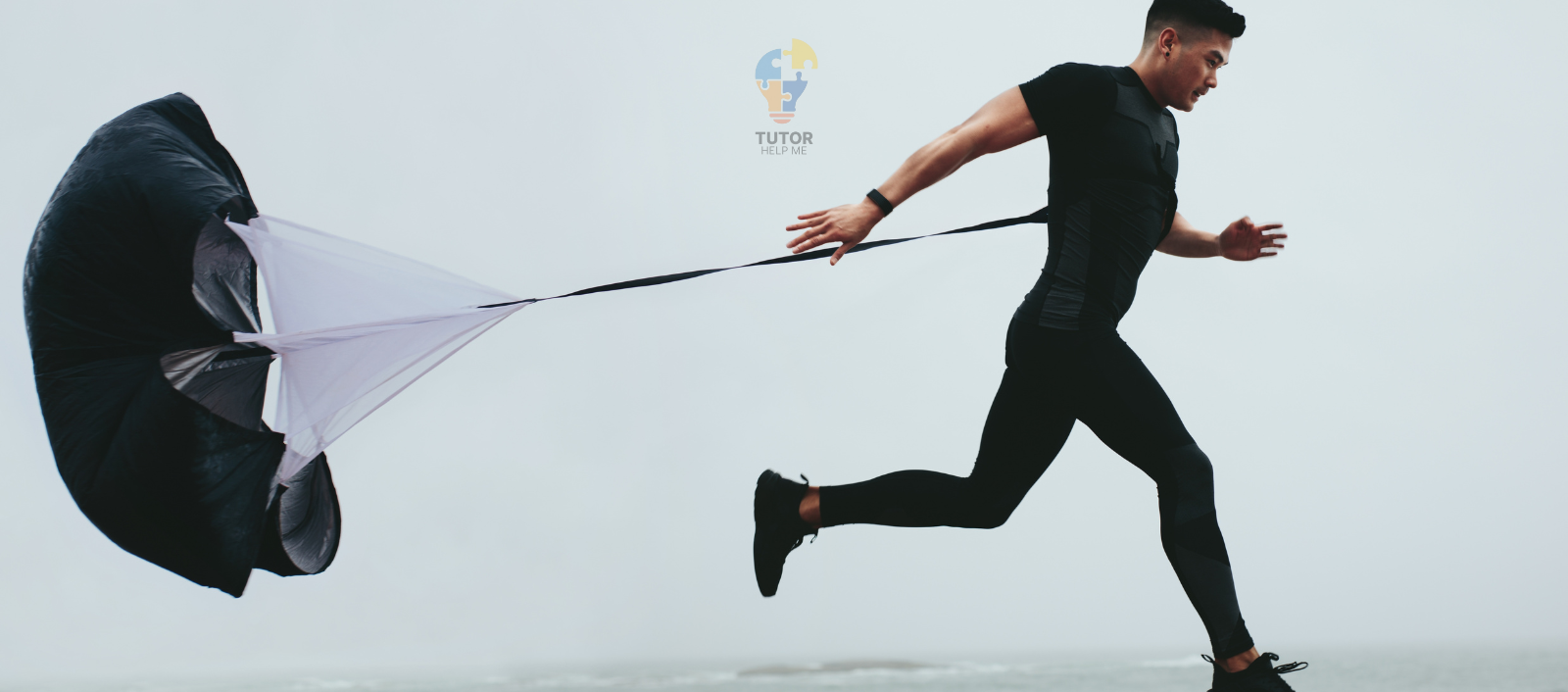

Now that you’ve seen how air can push back on moving objects, let’s see how all these forces come together to shape our daily lives.
How Forces Impact Our Lives
Forces are part of everything we do from getting out of bed to turning off the lights at night. They help us move, lift things, and use tools around us.
Knowing about different types of forces makes it easier to see how the world works. It turns everyday actions into simple science you can understand.
Pushing a swing uses gravity, tension, and applied force all at once. Even writing with a pen shows friction in action. These forces work quietly but make every task possible.
Why Choose Tutorhelpme Physics and Maths Tutor
- Expert Tutors: Highly skilled physics and maths tutor simplify complex topics.
- Personalised Learning: Lessons are tailored to match your pace and learning style.
- Interactive Sessions: Engage in dynamic online lessons with real-time feedback.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Build confidence in solving challenging problems efficiently.
- Exam Preparation: Receive targeted help for GCSE, A-Level, and other exams.
- Affordable Rates: Quality tutoring that fits your budget without compromising standards.
- Flexible Timings: Learn at times that work best for your busy schedule.
- Comprehensive Support: Tutors guide you through difficult concepts step by step.
- Boost Confidence: Overcome challenges and feel confident tackling any subject.
- Proven Results: Improve grades and achieve academic success with expert guidance.
Choose TutorHelpMe to unlock your potential in physics and maths!
Read More What is Force? Definition,SI unit and Types
FAQ’s
What is the strongest force in nature?
The strong nuclear force is the most powerful, holding atomic nuclei together.
What happens when forces are balanced?
When forces are balanced, an object stays still or moves at a constant speed.
What is the weakest force in nature?
Gravity is the weakest force, but it acts over long distances.
Can forces cancel each other out?
Yes, if two equal forces act in opposite directions, they cancel out, resulting in no movement.
How do forces help engineers design buildings?
Engineers calculate forces like gravity and wind resistance to make buildings stable and safe.