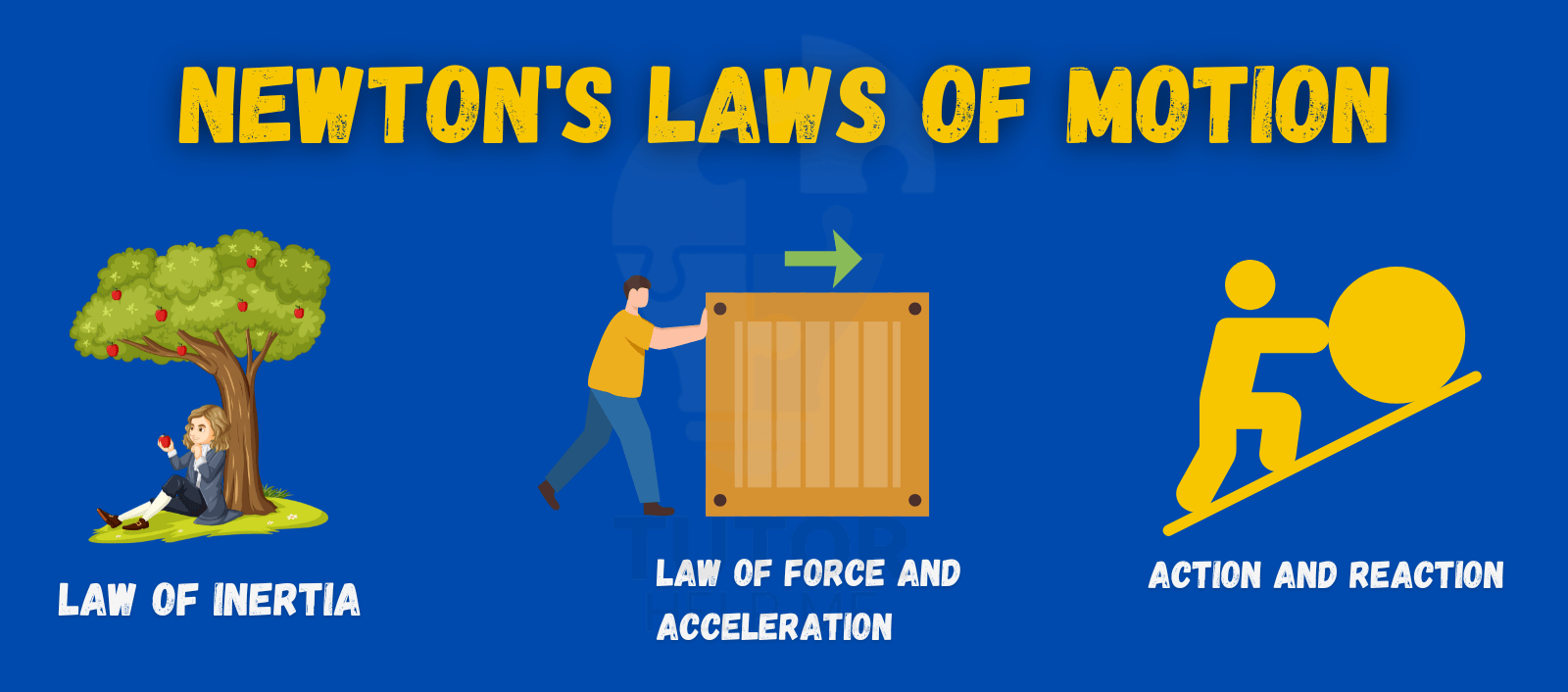
Newton’s Laws of Motion explain how things move and react. They apply to everyday actions like walking or driving.
The first law shows why things stay still or keep moving. The second explains how force changes speed or direction. The third shows how every action has an equal reaction.
Understanding these laws helps you see the science behind motion. Let’s explore each law and its real-life examples!
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Isaac Newton three laws explain how things move. Each law helps us understand how objects react to forces. Knowing these laws makes motion and physics simpler to understand.
Newton’s First Law of Motion:
Newton’s First Law of Motion explains inertia. It states that an object stays at rest or moves in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. This means objects resist changes to their motion unless something pushes or pulls them.
Everyday Examples
A Stationary Object
A book on a table stays there unless you move it. Gravity and the table’s surface balance out, keeping the book at rest.
A Moving Object
Imagine a ball rolling on a smooth surface. It keeps moving until friction or another force, like hitting a wall, stops it.

Driving a Car
When a car suddenly stops, passengers lurch forward. This happens because their bodies keep moving due to inertia, even as the car halts. Seat belts apply the needed force to stop this motion, ensuring safety.

Pulling a Tablecloth
When you quickly pull a tablecloth from under dishes, they remain still. This is because their inertia resists the sudden change in motion.
Newton’s First Law helps us understand everyday motion and why forces are essential to start or stop movement.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion:
Newton’s second law explains how force, mass, and acceleration are connected. It states that the force acting on an object equals its mass multiplied by its acceleration (F=ma). This helps us understand how objects move and respond to forces.
Everyday Examples
Riding a bicycle
Think of riding a bicycle. When you pedal harder, you apply more force, making the bike accelerate faster. If the bike is heavy or loaded with extra weight, you’ll need to apply more force to move it at the same speed.

Pushing a shopping trolley
Another example is pushing a shopping trolley. An empty trolley moves easily with a light push, but a fully loaded trolley requires more force to start moving or speed up.

Driving
Driving also reflects this law. Pressing the car’s accelerator increases the engine’s force, making the car accelerate. However, a heavier vehicle, like a truck, requires more force to reach the same speed as a small car.
Sports
Sports show this law too. Kicking a football hard increases its speed, while a heavier ball needs more force to achieve similar motion.

Newton’s second law is all around us. It explains everyday actions and helps us predict how objects will move when forces act on them.
Newton’s Third Law of Motion:
Newton’s third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means whenever one object exerts a force on another, the second object pushes back with the same force in the opposite direction.
Walking
When you step forward, your foot pushes against the ground. The ground pushes back with equal force, allowing you to move. Without this reaction, walking would be impossible.
Swimming
When you push water backward with your arms, the water pushes you forward. This equal and opposite force allows you to move through the water efficiently.

Rocket
Rocket launches clearly demonstrate this law. The rocket’s engines push exhaust gases downward. In return, the gases push the rocket upward, propelling it into the sky.
chair
Using a chair also shows this principle. When you sit, your body applies force on the chair. At the same time, the chair applies an equal and opposite force upward, supporting your weight.

Newton’s third law helps explain balance and movement in our daily lives. From driving to sports, every action has a reaction, making this law essential for understanding motion and forces.
Why Choose TutorHelpMe Physics and Maths Tutors
Expert Tutors: Learn from experienced Physics and Maths Tutor who simplify complex topics.
1-to-1 Attention: Get personalised lessons tailored to your needs.
Flexible Learning: Schedule sessions that fit your busy life.
Improved Results: Boost your confidence and achieve better grades.
Interactive Methods: Engage with fun and practical learning approaches.
Comprehensive Support: Get help with homework, exams, and problem-solving.
Affordable Rates: Quality tutoring without breaking the bank.
Online Convenience: Access top tutors from the comfort of your home.
Customised Plans: Learn at your pace with personalised study plans.
Proven Success: Trusted by many students for academic improvement.