The nervous system is a complex system that controls the body’s activities, allowing it to respond to changes in the environment. It is responsible for essential functions such as movement, sensation, and thought. Made up of the brain and spinal cord, along with a network of nerves that branch off to various parts of the body, the nervous system is critical for maintaining body functions. It has two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Structure of the Nervous System
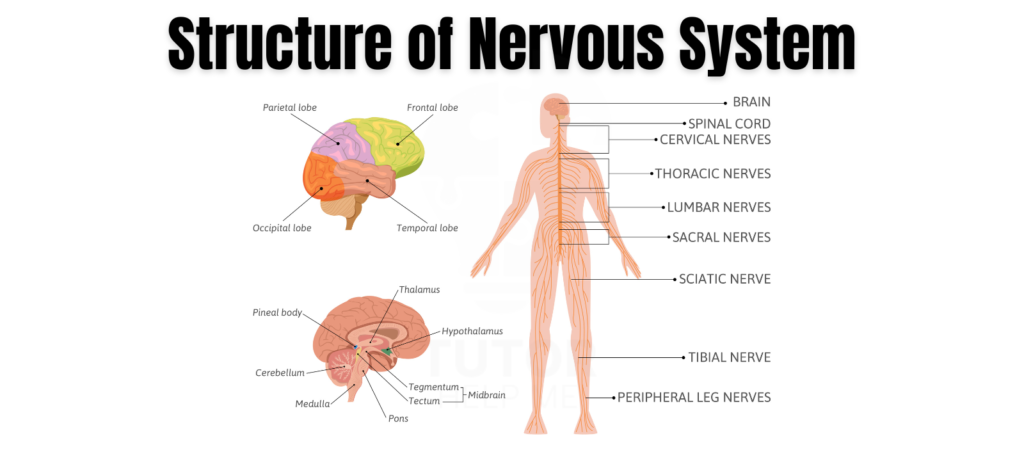
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The central nervous system is made up of your brain and spinal cord. It processes information received from the body and coordinates responses.
Brain
The brain is the control center of the nervous system. It consists of different parts of the brain, such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem, each responsible for various functions like memory, coordination, and vital bodily processes.
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord connects the brain to the rest of your body. It plays a vital role in transmitting signals from your brain to other parts of your body and vice versa. The spinal cord is essential for reflex actions and helps you move efficiently.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The peripheral nervous system includes the nerves that branch off from the spinal cord to reach different parts of the body. It is divided into two main parts:
Sensory (Afferent) and Motor (Efferent) Neurons
Sensory neurons send signals from various parts of your body to the brain, while motor neurons carry instructions from the brain to muscles and glands.
Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems
- Somatic Nervous System: Controls voluntary movements like walking or picking up objects.
- Autonomic Nervous System: Regulates involuntary functions, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the sympathetic (fight or flight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest) systems.
Functions of the Nervous System
The nervous system plays a central role in controlling the body. Its main functions include:
Sensory Input
The nervous system gathers sensory input from the environment through sensory neurons. These neurons send signals to the brain, enabling you to sense and interpret stimuli like temperature, light, and sound.
Integration
The brain processes sensory input and integrates it with existing information to decide on an appropriate response. This integration helps in memory formation and decision-making.
Motor Output
After processing information, motor neurons send signals from your brain to muscles and glands, resulting in actions such as movement or secretion of hormones.
Homeostasis
The autonomic nervous system helps regulate internal conditions like body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure, ensuring the body remains in balance.
Higher Brain Functions
The brain is responsible for cognition, emotions, language, and problem-solving, which are crucial for human interaction and survival.
Common Nervous System Disorders
Neurological Disorders
- Alzheimer’s Disease: A progressive disorder that affects memory and cognitive abilities. It occurs due to the degeneration of neurons in the brain.
- Parkinson’s Disease: A condition caused by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons, leading to motor control issues such as tremors and stiffness.
- Epilepsy: Characterized by recurring seizures due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
Injuries to the Nervous System
- Spinal Cord Injury: Damage to the spinal cord can result in partial or complete paralysis. Rehabilitation often focuses on restoring mobility and independence.
- Traumatic Brain Injury: This occurs when the brain is injured due to an impact or blow, leading to cognitive and behavioral changes.
Infections and Autoimmune Disorders
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, often caused by infections.
- Multiple Sclerosis: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath of nerve fibers, disrupting communication between the brain and the body.
“Get sucess in Gcse and A-level with our 1-On-1 Biology tutors“
Diagnosis and Treatment of Nervous System Disorders
Diagnostic Tools
- Imaging Techniques: MRI and CT scans help visualize the brain and spinal cord to detect abnormalities such as tumors or injuries.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): Measures electrical activity in the brain to diagnose conditions like epilepsy.
- Neurological Exams: Assess reflexes, muscle strength, and coordination to identify potential issues.
Treatment Options
- Medications: These can help manage symptoms by regulating neurotransmitter activity or reducing inflammation. Examples include antiepileptic drugs and dopamine replacements for Parkinson’s.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to remove tumors, relieve pressure, or correct structural problems.
- Therapies: Physical, occupational, and speech therapies play a crucial role in recovery and improving quality of life.
Tips for Nervous System Health
Maintaining a healthy nervous system is essential for overall well-being. Here are some tips:
- Balanced Diet: Include foods rich in vitamins B12, E, and omega-3 fatty acids to support nerve health.
- Regular Exercise: Promotes blood flow to the brain and spinal cord, enhancing nerve function.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation and deep breathing reduce the harmful effects of chronic stress on the nervous system.
- Avoid Neurotoxins: Limit exposure to substances like excessive alcohol and recreational drugs that can damage nerves.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is vital for nerve function and overall health.
Conclusion
The nervous system is a remarkable and complex network that controls every aspect of the body’s functioning. Understanding its structure, functions, and common disorders highlights its importance in maintaining overall health. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking timely medical care for any issues, individuals can ensure their nervous system remains in optimal condition.
Read More Human Digestive System – Structure, Functions, and Common Issues
FAQ’s
What are 3 symptoms of a weak nervous system?
Three symptoms of a weak nervous system include persistent fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and muscle weakness or tremors affecting coordination.
How do I get my nervous system back to normal?
Restore your nervous system by managing stress, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, staying hydrated, and getting adequate sleep daily.
How can I treat my nervous system at home?
Treat your nervous system at home with relaxation techniques, deep breathing, yoga, healthy meals, proper hydration, and regular exercise.

