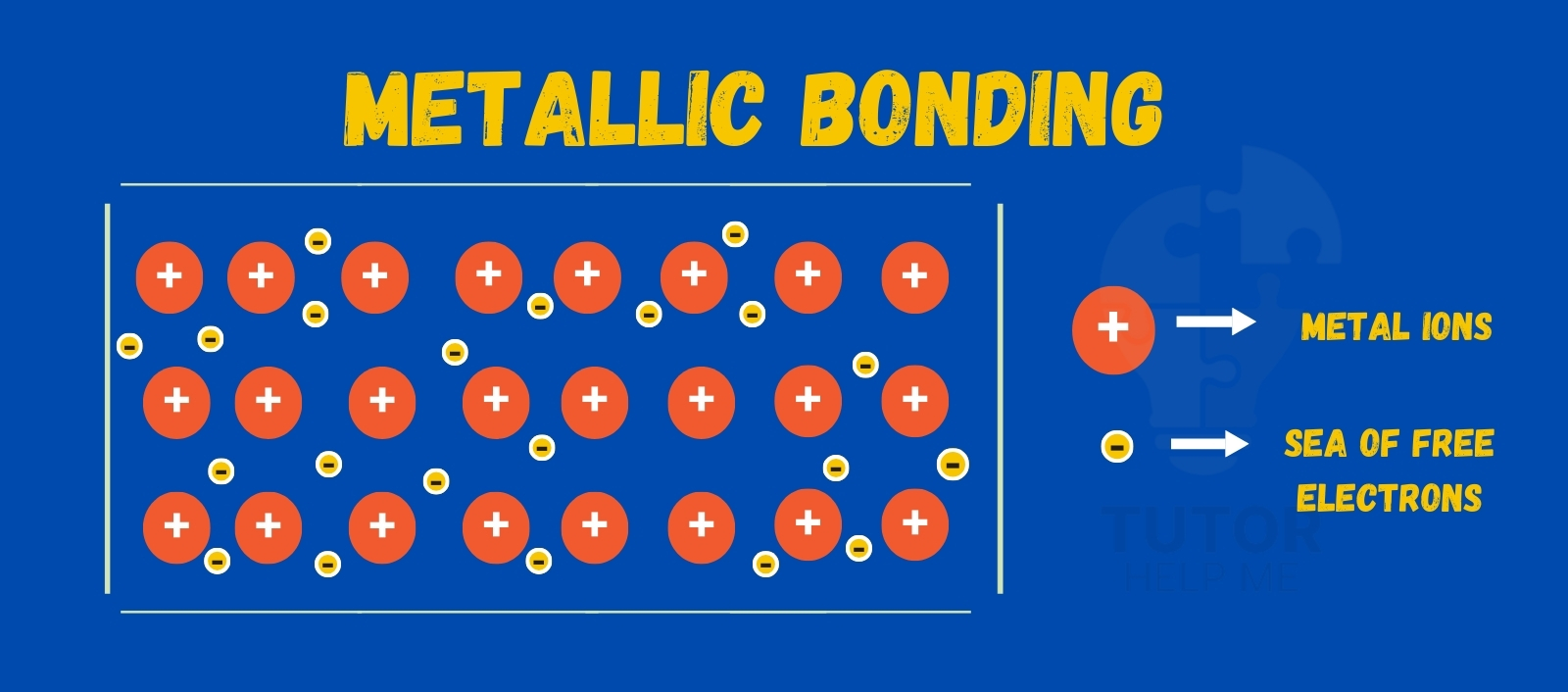
Metallic bonds are the key to understanding metals. They form when metal atoms share electrons freely. This creates unique properties like conductivity and malleability.
Metals are shiny and can be shaped easily because of these bonds. Learning about metallic bonds helps you see why metals are so useful.
In this blog you will learn What Are Metallic Bonds, their Examples, Properties and Formation.
What Are Metallic Bonds?
A metallic bond is the attraction between positive metal ions and a sea of free electrons.
In metallic bonding:
- Electrons are not held by one atom
- Electrons move freely between atoms
- This “sea of electrons” holds metal atoms together
This is why metals behave the way they do.
If you are new to this topic, start by learning what bonds are and the main types of bonds or book a free assessment with chemistry tutors.
Mettalic Bonding in Copper
Copper is known for carrying electricity very well. This is because of its metallic bonds. In copper, electrons move freely around copper ions. This forms a “sea of electrons.”
These free electrons help copper carry electricity easily. That’s why copper is used in wires and electric parts.
Copper can also bend without breaking. It can be made into thin wires. This is because metallic bonds let copper ions slide past each other.
Copper is shiny because the sea of electrons reflects light. It also does not rust easily. When copper touches air, it forms a thin layer. This layer protects it from rust.
Because of metallic bonds, copper can carry electricity, bend easily, stay shiny, and last a long time.
Equation:
Cu(s)+O2(g)→CuO(s)
Copper reacts with oxygen to form a protective copper oxide layer.
Mettalic Bonding in Aluminum
Aluminum is light but strong. This makes it useful in many ways. Its metallic bonds let electrons move freely. This helps it carry electricity well and resist rust.
Because it is light and strong, aluminum is used in airplanes. These bonds give it the right mix of strength and lightness.
Aluminum can be shaped easily. It can be made into thin sheets or detailed parts. It does not break when shaped. This helps in making cans, car parts, and building materials.
Aluminum is shiny too. The free electrons reflect light. This shine makes it good for decoration and helps buildings stay cool by reflecting sunlight.
Aluminum also makes a thin layer on its surface. This layer keeps it safe from rust. That’s why aluminum lasts a long time.
Equation:
4Al(s)+3O2(g)→2Al2O3(s)
Aluminum reacts with oxygen to form a protective aluminum oxide layer.
Properties of Metallic Bonds
Conductivity
- Metals conduct electricity because their electrons move freely. In a metallic bond, electrons are not bound to any specific atom. Instead, they form a ‘sea’ around positive metal ions.
- This allows electrons to flow easily when an electric field is applied, resulting in high electrical conductivity.
- For example, copper is commonly used in electrical wiring due to its excellent conductivity.
This property is essential for various applications, from household wiring to electronic devices, ensuring efficient energy transfer and functionality.
Malleability
- Malleability refers to a metal’s ability to be shaped without breaking. This property arises from the sliding of metal ions past each other within the ‘sea of electrons.’
- When a metal is hammered or rolled, the ions shift, but the metallic bonds hold them together.
- For instance, gold can be hammered into thin sheets known as gold leaf.
Malleability is crucial for manufacturing processes that involve shaping metals into products like car bodies, foil, and structural components.
Luster
- The ‘sea of electrons’ in metallic bonds reflects light, giving metals their shiny appearance, known as luster.
- When light hits a metal surface, the free electrons absorb and re-emit photons, creating a reflective sheen.
- This property makes metals like silver and aluminum ideal for decorative applications, mirrors, and jewelry.
Luster also enhances the aesthetic appeal of metallic objects, contributing to their value and desirability in various industries.
Ductility
- Ductility is the ability of metals to be drawn into thin wires without breaking. This property is due to the capacity of metal ions to slide past each other within the ‘sea of electrons’ without disrupting the metallic bond.
- For example, copper and aluminum are highly ductile and commonly used in electrical wiring.
Ductility is essential for applications that require metals to be stretched into thin forms while maintaining strength and conductivity.
Thermal Conductivity
- Metals conduct heat efficiently due to the free movement of electrons within their structure.
- In metallic bonds, electrons transfer kinetic energy rapidly, enabling quick heat distribution.
- This property is vital for applications like cookware, heat sinks, and radiators.
For instance, copper and aluminum are often used in pots and pans because they distribute heat evenly, preventing hotspots and ensuring efficient cooking.
High Melting and Boiling Points
- Metals generally have high melting and boiling points due to the strong bonds between metal ions and the ‘sea of electrons.’
- These bonds require substantial energy to break. For example, tungsten has an extremely high melting point, making it suitable for use in light bulb filaments.
High melting and boiling points are crucial for materials exposed to extreme temperatures, ensuring durability and performance in demanding environments.
Density
- Metals typically have high density, meaning they are heavy and strong. This property results from closely packed metal ions in the metallic bond.
- For example, lead is very dense and is used in applications requiring substantial weight, like radiation shielding.
High density contributes to the strength and durability of metals, making them suitable for construction, manufacturing, and various industrial applications.
Magnetism
- Some metals, such as iron, cobalt, and nickel, exhibit magnetic properties due to their metallic bonds. In these metals, the alignment of electron spins creates a magnetic field.
This property is essential for applications like electric motors, transformers, and magnetic storage media.
Magnetism in metals is utilized in various technologies, from household appliances to advanced electronic devices.
Tensile Strength
- Tensile strength refers to a metal’s ability to withstand significant stretching or pulling forces without breaking.
- This property is crucial for construction materials, where metals must support heavy loads and withstand stress.
- For example, steel has high tensile strength, making it ideal for building skyscrapers, bridges, and other structures.
Tensile strength ensures the safety and stability of infrastructure and machinery.
Reflectivity
- Metals reflect light effectively due to the free electrons in their structure. This property makes metals useful for mirrors and reflective surfaces.
- For instance, aluminum’s reflectivity is utilized in telescope mirrors and solar reflectors.
Reflectivity enhances the efficiency of optical devices and solar energy systems by directing and focusing light precisely.
Sonority
- Metals produce a ringing sound when struck, known as sonority. This property is due to the ability of metal ions to vibrate within the ‘sea of electrons.’
- For example, bells and musical instruments like cymbals and brass instruments rely on the sonorous quality of metals.
Sonority adds to the cultural and practical value of metals in creating musical and signaling devices.
Corrosion Resistance
- Some metals form protective oxide layers that prevent further corrosion, enhancing their longevity.
- For example, aluminum develops a thin oxide layer that shields it from environmental damage.
- Stainless steel, which contains chromium, forms a protective layer that resists rust.
Corrosion resistance is crucial for metals used in construction, transportation, and outdoor applications, ensuring durability and reduced maintenance.
How Are Metallic Bonds Formed?
Metal Atoms Group Together: Metal atoms come close, ready to share electrons.
Electrons Delocalize: Valence electrons from the metal atoms become free-moving.
Formation of Positive Ions: Metal atoms lose some electrons, turning into positive ions.
Sea of Electrons Forms: The delocalized electrons create a “sea” around these positive ions.
Attraction Between Ions and Electrons: The positive ions attract the free electrons, creating a strong bond.
Metallic Lattice Formation: This attraction forms a lattice structure, resulting in the unique properties of metals.
How to Visualise Metallic Bonding
Think of metal atoms as:
- Positive ions arranged in a lattice
- Electrons flowing around like a sea
The electrons act like glue that holds the metal together.
This model explains metal behaviour clearly.
Common Mistakes
Students often think:
- Metallic bonds involve shared pairs like covalent bonds
(Wrong — electrons are delocalised) - Metals do not have bonds at all
(Wrong — metallic bonds are strong attractions)
Getting this right helps improve marks.
Quick Exam Tip
In exams:
- Use the phrase “sea of delocalised electrons”
- Explain why electrons are free
- Link bonding to electrical/thermal conductivity
Short, accurate answers score more marks.
Why Choose Tutorhelpme Chemistry Tutors
Expert Tutors: Experienced Chemistry Tutors with strong academic backgrounds.
Personalized Learning: Customized lessons to meet individual needs.
Flexible Scheduling: Sessions at convenient times for students.
Interactive Lessons: Engaging, hands-on teaching methods.
Proven Results: Track record of improved grades and understanding.
Affordable Rates: Competitive pricing for quality education.
Comprehensive Support: Assistance with homework, projects, and exam prep.
Modern Resources: Use of the latest educational tools and technology.
Continuous Feedback: Regular progress updates and constructive feedback.
Supportive Environment: Encouraging tutors who build student confidence.
Read More What Is an Ionic Bond? Types, Formation, and Properties
FAQ’s
what are sea of electrons?
“Sea of electrons” describes freely moving electrons among metal atoms, enabling metallic properties.
Which elements form metallic bonds?
Metallic bonds form between metal atoms like copper, iron, aluminum, and gold.
Why do metals conduct electricity?
Because free electrons in metallic bonds move easily and carry electric current.
Why are metals shiny?
The “sea of electrons” reflects light, which gives metals their shiny surface.
Can metallic bonds break easily?
No, they are strong and do not break easily. That’s why metals are tough and durable.
Why are metals malleable and ductile?
Because metal atoms can slide over each other without breaking the bond, making them easy to bend or stretch.
Why do metals have high melting points?
Strong attraction between ions and electrons needs lots of energy to break.