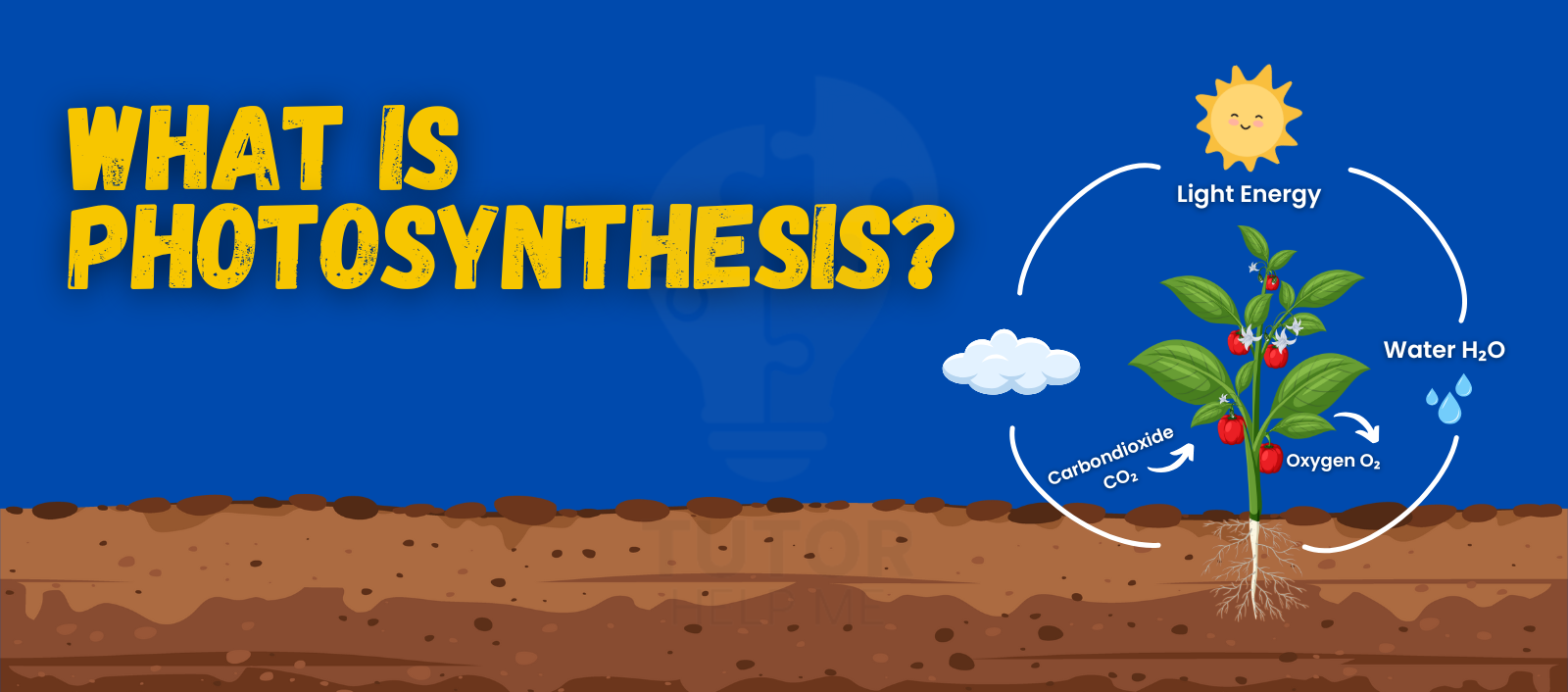
Photosynthesis is the way plants, algae, and some bacteria change light into energy.
This process makes oxygen and glucose, both essential for life.
By learning about photosynthesis, you can see how it supports ecosystems and balances the carbon cycle.
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is how plants make food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
This process creates glucose and oxygen, which support life on Earth.
By understanding photosynthesis, you can see how it fuels growth and provides oxygen for all living things.
The energy from sunlight is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
The basic equation of photosynthesis can be written as:
6CO2 + 6H2O light→ C6H12O6 + 6O2
This process is crucial for removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and maintaining oxygen levels.
It is also the foundation of the food chain, as plants store the chemical energy produced during photosynthesis for themselves and other organisms.
Let’s now explore where photosynthesis takes place and how it happens inside plant cells.
Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place?
- Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts found in plant and algae cells.
- Chlorophyll, a green pigment, absorbs sunlight to start the process.
- Light energy splits water into oxygen, hydrogen, and electrons.
- The energy is stored in ATP and NADPH, later used in the Calvin cycle to make glucose.
- In plants and algae, photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts.
- In bacteria, it happens in special cell membranes.
- This ability to change light into energy helps organisms live in many environments.
Now lets learn the process of photosynthesis and how each step works.
The Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis occurs in two main stages:
- Light-dependent reactions
- Light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
These steps explain how plants turn sunlight into food. This clear process will help you understand each stage easily.
1. Light-Dependent Reactions
- Take place in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts.
- Chlorophyll absorbs light, exciting electrons to make ATP and NADPH.
- These reactions need light and water.
- During this stage, water splits into oxygen gas, hydrogen ions, and electrons.
- Oxygen gas produced by photosynthesis is released into the air, helping us breathe.
- ATP and NADPH store energy for the next stage.
2. Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
- Happen in the stroma of the chloroplast.
- Do not require light to occur.
- Use ATP and NADPH to turn carbon dioxide into glucose.
- Carbon fixation starts the process by capturing carbon dioxide.
- The reactions make glucose, stored as starch or used for energy.
- This stage shows how plants change light energy into food for survival.

Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis provides numerous benefits that make life on Earth possible:
- Oxygen Production: The oxygen in the atmosphere is produced by photosynthesis, supporting the survival of all aerobic organisms.
- Food Source: Glucose produced during photosynthesis serves as a primary energy source for plants and animals.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: Photosynthesis reduces carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, balancing gas exchange and mitigating climate change.
- Energy Storage: Plants store energy from photosynthesis as starch, which is consumed by other organisms.
Photosynthesis is essential not only for individual plants but also for maintaining global ecological balance.
It supports the global carbon cycle, regulates carbon dioxide levels, and provides energy for nearly all living organisms.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is influenced by various environmental and internal factors that impact the rate at which plants produce glucose and oxygen. Let’s look at the key factors:
1. Light Intensity
- Plants need light for photosynthesis.
- More light increases the rate until it reaches a limit.
- Too much light can harm chlorophyll and reduce efficiency.
2. Carbon Dioxide Concentration
- Carbon dioxide is a main reactant in photosynthesis.
- Higher levels increase the rate if light and temperature are good.
3. Water Availability
- Water is needed in light-dependent reactions.
- Without enough water, plants cannot release oxygen or make energy.
- Long droughts can fully stop photosynthesis.
4. Temperature
- Enzymes work best in a certain temperature range.
- Low heat slows the process.
- Very high heat destroys enzymes and stops photosynthesis.
5. Chlorophyll Content
- Chlorophyll absorbs light for photosynthesis.
- Plants with more chlorophyll make food faster.
6. Environmental Factors
- Pollution, soil, and air changes affect photosynthesis.
- Pollutants can block light or change carbon dioxide levels.
By understanding these factors, we can manage agricultural practices to maximize crop yields and promote healthier ecosystems.
Real-Life Applications of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis has practical importance beyond its natural role in sustaining ecosystems. Here are some examples:
- Agriculture: Photosynthesis directly affects crop production. Farmers monitor light, water, and nutrients to ensure plants photosynthesize efficiently, increasing food supply.
- Renewable Energy: Scientists are researching artificial photosynthesis to produce clean energy by mimicking natural processes.
- Climate Regulation: Photosynthesis helps absorb excess carbon dioxide, playing a key role in controlling global warming.
- Food Chains: As the primary producers, plants support herbivores and other animals by providing energy through photosynthesis.
- Medicinal Uses: Algae, which carry out photosynthesis, are used in pharmaceuticals for their health benefits.
These applications highlight how photosynthesis is not only vital for survival but also provides solutions to global challenges.
Common Misconceptions About Photosynthesis
Some misconceptions about photosynthesis often lead to confusion:
- Photosynthesis Only Happens During the Day: While the light-dependent reactions require sunlight, the Calvin cycle can occur in the absence of light.
- Plants Only Produce Oxygen: Plants also consume oxygen during respiration but produce more oxygen than they use.
- Photosynthesis is Exclusive to Green Plants: Many organisms, including algae and some bacteria, also carry out photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll is the Only Pigment: While chlorophyll is the main pigment, others like carotenoids also play a role in absorbing light.
Clearing these myths helps us better understand the process and its significance.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is the process that powers life on Earth. It allows plants, algae, and some bacteria to turn sunlight into food and oxygen.
By learning what is photosynthesis, we understand how it supports ecosystems, maintains the carbon cycle, and provides energy for all living things.
Read More What is Cell? Types, Function and Structure
FAQ’s
What is the main purpose of photosynthesis?
The main purpose of photosynthesis is to convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored as glucose.
This process provides energy for plants, algae, and some bacteria to grow and survive. Photosynthesis also releases oxygen as a by-product, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms.
It plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere.
Can photosynthesis occur without sunlight?
No, photosynthesis cannot occur without sunlight. Sunlight provides the energy needed for the light-dependent reactions, which are the first stage of photosynthesis.
During this stage, chlorophyll absorbs light to produce energy-rich molecules like ATP and NADPH. These molecules are then used in the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
Without sunlight, the process cannot begin, and plants, algae, and other photosynthetic organisms cannot create food or release oxygen.
Why is chlorophyll green?
Chlorophyll is green because it absorbs most of the red and blue light from sunlight but reflects green light. This reflection makes chlorophyll appear green to our eyes.
Chlorophyll’s ability to absorb specific wavelengths of light is crucial for photosynthesis, as it captures the energy needed to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Its green color is a result of the specific pigments it contains, which are optimized for efficient light absorption.
What is ATP and NADPH?
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) and NADPH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) are energy-carrying molecules produced during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
ATP: Known as the “energy currency” of the cell, ATP provides the energy required for various cellular processes, including the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis.
NADPH: This molecule carries high-energy electrons and is used in the Calvin cycle to reduce carbon dioxide into glucose.
Both ATP and NADPH store the energy captured from sunlight and make it available for the next stage of photosynthesis, ensuring the process continues efficiently.